The Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic has played a major role in changing learning and working methods, worker reskilling, the transformation of supply chains and expansion of the gig economy. While these changes were born of necessity during lockdown, they are expected to serve a pivotal role in future business dynamics globally.
Online learning is here to stay, beyond COVID-19
The pandemic has severely disrupted face-to-face studies globally, forcing universities and students to adapt to online learning. Online course providers such as Coursera and edX have surged in popularity, as lockdowns have left people with more free time and increasing demand for new skills, particularly in digital literacy. Conventional universities are also likely to expand their online learning offerings, as well as provide more flexible hybrid studies. In fact, nearly three out of four respondents of a World Economic Forum‘s survey in 2020 said they expect higher education to become a hybrid combination of in-person and online learning by 2025.
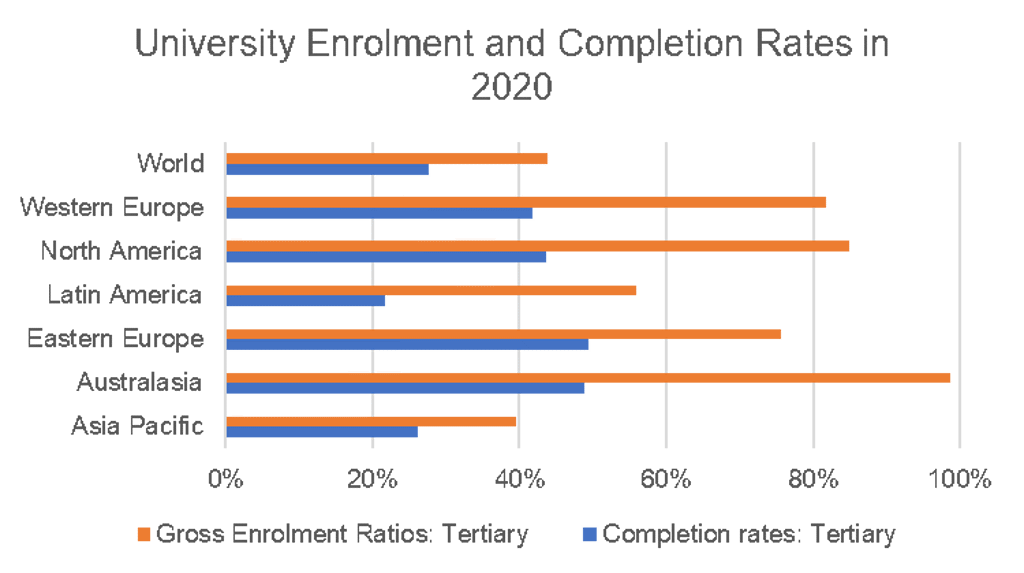
Source: Euromonitor International from UNESCO/Eurostat/OECD/national statistics
North America and Western Europe remain leaders in tertiary education enrolment. However, rising drop-out rates are resulting in lower completion rates. The value of having a university degree risks depreciation, as both students and businesses increasingly appreciate hands-on experience. For example, major global companies, particularly in the engineering and IT sectors, such as Tesla, Google, Netflix and Apple to name a few, have eliminated university degree requirements for new employees.
Pandemic exposes the need for better work-life balance
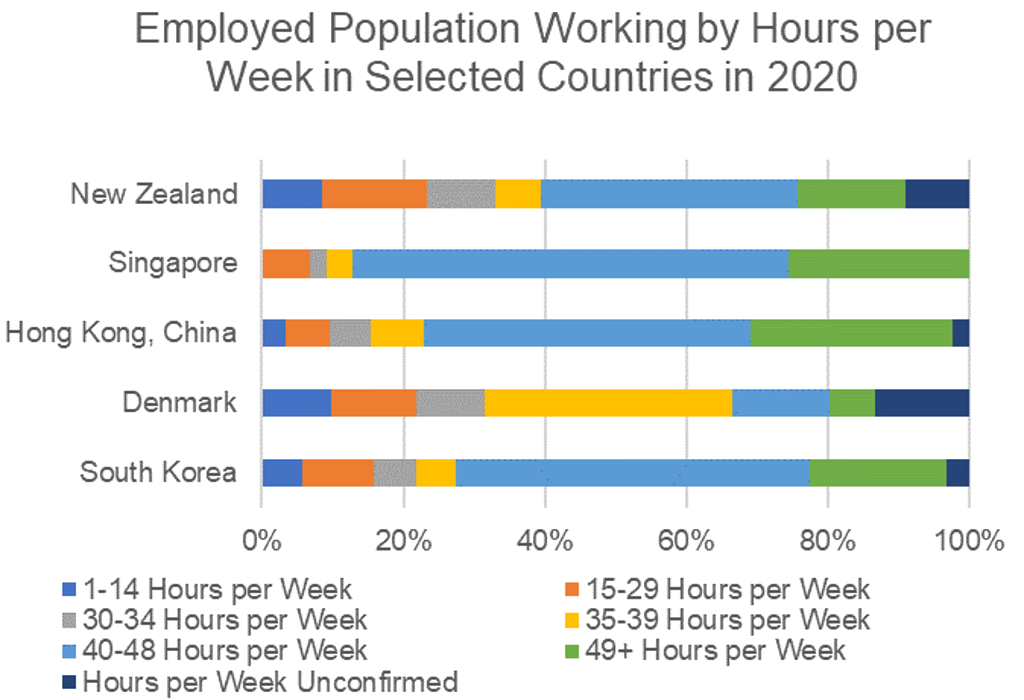
The work-life balance has seen some improvements in the last decade in majority of developed countries, with governments imposing limits on overtime hours or companies themselves reducing the numbers of working days per week. In 2020, Microsoft Japan tested a four-day week and reported a significant boost in productivity. However, this contrasts with many Asian countries, where employees in Singapore, Hong Kong and South Korea are working among the longest hours per week. As of 2020, more than one in four workers in Singapore and Hong Kong worked more than 49 hours a week, while in South Korea this number stood at nearly 20% of the employed population.
Source: Euromonitor International from International Labour Organisation (ILO)
Alongside attempts to shorten working hours, the pandemic has fostered remote working on a global scale. While some companies were reluctant to shift to teleworking at first, worker safety and the need to ensure work continuity have necessitated the flexibility of home working. Despite vaccination rollouts, more than three in four employees still expect to work at least three days a week remotely. Expanding remote working is anticipated not only to improve work-life balance, but also allow to cut costs on office space rental and utilities, as well as worker commutes.
COVID-19 drives the need for worker reskilling
Falling numbers of graduates in technical fields have been amplifying the skills gap in labour markets for over a decade. Education systems can be quite rigid, unable to adapt quickly to the evolving needs of the labour market. Moreover, young people tend to choose higher education in higher, value-added fields, resulting in a shortage of low-skilled labour in developed countries. During the pandemic and closure of state borders, some countries including Germany, the US, Canada and Australia, which greatly rely on immigrant workers, saw severe disruption in labour-intense industries, such as manufacturing and construction.
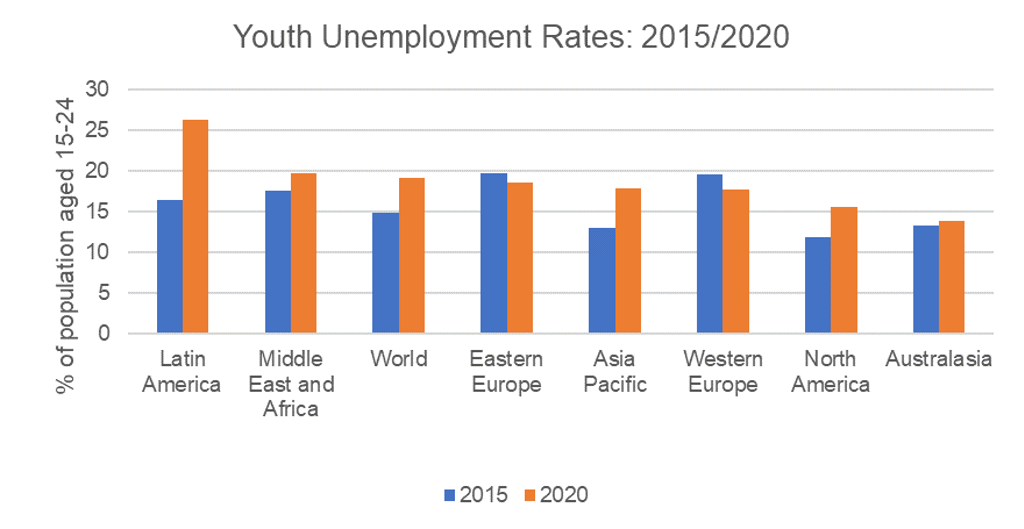
The COVID-19 outbreak prompted workers and governments to invest in reskilling, as many sectors were shut down, while others saw expanding demand in labour. Unemployment surged by 12.6% globally in 2020, with young workers seeing the sharpest drop in employment levels. To encourage young adults to re-join the labour market and shift their field of work, many countries have invested in worker retraining programmes, with a primary focus on digital literacy, technical and IT skills.
Source: Euromonitor International from International Labour Organisation (ILO)/Eurostat/national statistics
Flourishing remote work boosts opportunities for skilled freelancers
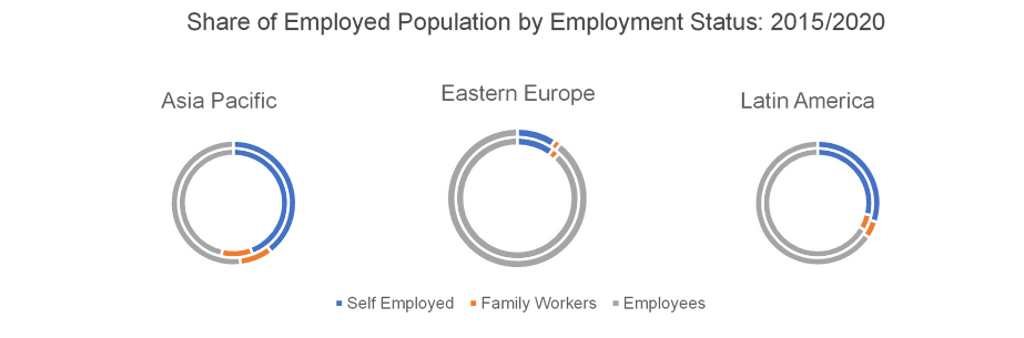
The gig economy is set to remain dominated by unskilled labour, yet remote work offers freelancing opportunities for highly skilled professionals as well. In the light of booming unemployment during COVID-19 and lockdown, skill matching platforms helped to reallocate labour from sectors shut down by the pandemic, such as tourism, accommodation and catering, and those with fast-rising demand, like agriculture and delivery.
Note: Inner circle represents data in 2015; outer circle represents 2020 data. Source: Euromonitor International from International Labour Organisation (ILO)
Skilled workers remain slow to adjust to potential in the gig economy, still preferring full-time employment rather than freelance opportunities. However, given remote work has flourished during quarantine, many employers and employees would prefer to continue working outside of the office environment, providing great opportunities for skilled professionals to enter a knowledge-based gig economy.
Expanding online presence and supply disruption during COVID-19 results in relocated production, closer to the end-user
In 2020, global supply chains saw major disruption due to closed state borders, cancelled commercial flights and interrupted manufacturing in many countries. To safeguard future supply chains, ensure business continuity and diminish reliance on Asian manufacturing facilities, global companies are restructuring and diversifying their supply channels. Firms are beginning to bring production facilities closer to home to accommodate B2B, B2G and B2C demand quicker and with less potential logistic disruption. But, expanding online shopping puts increasing pressure on swift logistics, as consumers expect fast delivery of their online purchases.
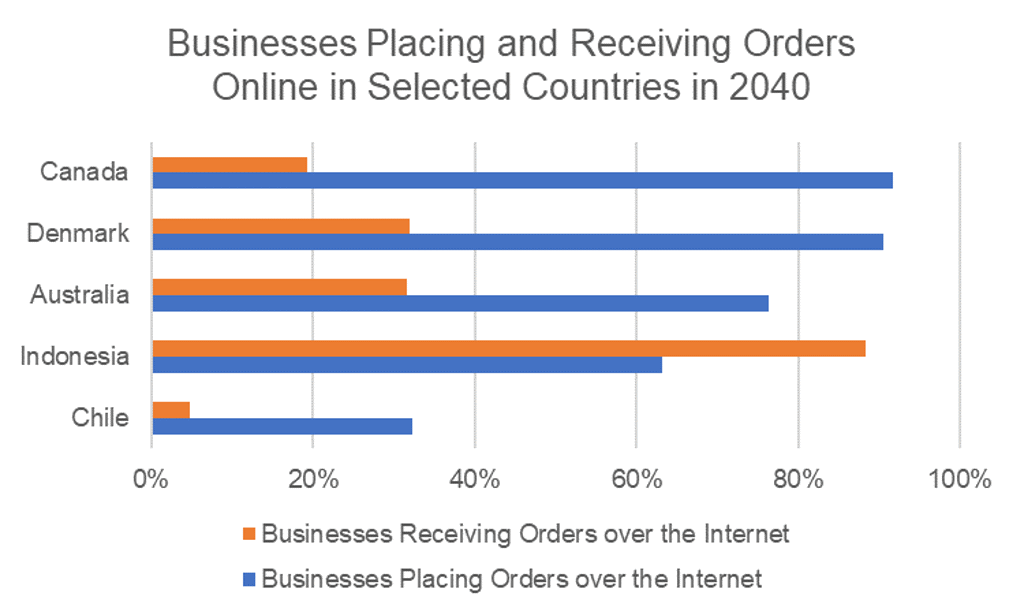
Source: Euromonitor International from UNCTAD, Eurostat
Online orders saw a major uptick during the quarantine and are expected to remain a vital part of shopping experiences in the future. As an example, Indonesia recorded a 16.7 percentage point increase in businesses receiving orders online over 2015-2020 and the figure is expected to reach 88.4% by 2040. Alongside expanding online shopping, Indonesia is also heavily investing in its infrastructure and logistic capabilities, adding to smooth online purchase deliveries. In fact, Indonesia climbed from 55th position (out of 160) in the Logistics Performance Index in 2015 to 48th in 2020.
To learn more about how consumers and businesses will operate in a post-pandemic world, register for the upcoming live webinar, The World Beyond the Pandemic.